Abstract
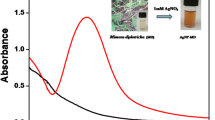
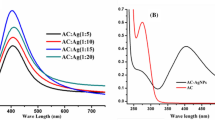
Heavy metal-based pollutants are one of the most alarming health hazards causing multiple diseases including cancer, hepatotoxicity, brain hemorrhage, kidney and heart failures, etc. In this study, we report an ecofriendly, low cost, and simple synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) mediated by Nannorrhops ritchiana leaf-based biomolecular extract as a key biosensor for the mercury(II) heavy metal. The formation of AgNPs was confirmed by using different characterization techniques including UV–visible spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscopy. The synthesized AgNPs are yellowish-brown and exhibit the surface plasmon resonance around 435 nm. The various functional groups responsible for reduction of Ag+ to Ag0 and capping agents present in the leaf extract were confirmed by infrared spectroscopy. Energy-dispersive X-ray and scanning electron microscopic analysis were used to confirm the presence of silver and surface morphology of the nanoparticles, respectively. X-ray diffraction data suggested crystalline nature of the prepared nanoparticles. The AgNPs were successfully applied as a sensitive and selective platform for sensing of mercury(II) ions. Various parameters including nanoparticles loading, concentration of Hg+2, pH, and reaction time were optimized. The platform demonstrates a low limit of detection (4.8 × 10–7 M) and limit of quantification (4.8 × 10–7 M) with an R2 value of 0.999. The SS-DNA interaction with the AgNPs, studied by UV–Vis spectroscopy revealed intercalative mode of binding with a binding constant of 1.04 × 104 units. Importantly, this AgNPs platform also demonstrated good antibacterial efficacy against Proteus mirabilis, Shigella flexneria, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGillicuddy, E.; Murray, I.; Kavanagh, S.; Morrison, L.; Fogarty, A.; Cormican, M., et al.: Silver nanoparticles in the environment: Sources, detection and ecotoxicology. Sci. Total Environ. 575, 231–246 (2017)
Baghayeri, M.; Amiri, A.; Motamedifar, A.: Investigation about electrocatalytic oxidation of glucose on loaded Ag nanoparticles on functionalized carbon nanotubes. Ionics 22, 1709–1717 (2016)
Baghayeri, M.; Nodehi, M.; Amiri, A.; Amirzadeh, N.; Behazin, R.; Iqbal, M.Z.: Electrode designed with a nanocomposite film of CuO honeycombs/Ag nanoparticles electrogenerated on a magnetic platform as an amperometric glucose sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 1111, 49–59 (2020)
Baghayeri, M.; Nabavi, S.; Hasheminejad, E.; Ebrahimi, V.: Introducing an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Two Layers of Ag Nanoparticles Decorated Graphene for Rapid Determination of Methadone in Human Blood Serum. Top. Catal. 65, 623–632 (2022)
Baghayeri, M.; Veisi, H.; Farhadi, S.; Beitollahi, H.; Maleki, B.: Ag nanoparticles decorated Fe3O4/chitosan nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization and application toward electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 15, 1015–1022 (2018)
Bello, B.A.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, J.A.; Syed, F.Q.; Mirza, M.B.; Shah, L., et al.: Anticancer, antibacterial and pollutant degradation potential of silver nanoparticles from Hyphaene thebaica. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 490, 889–894 (2017)
Tien, D.; Liao, C.; Huang, J.; Tseng, K.; Lung, J.; Tsung, T., et al.: Novel technique for preparing a nano-silver water suspension by the arc-discharge method. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 18, 750–756 (2008)
Mafune, F.; Kohno, J.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Sawabe, H.: Formation and size control of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 9111–9117 (2000)
Yin, B.; Ma, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.: Electrochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles under protection of poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone). J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 8898–8904 (2003)
Pingali, K.C.; Rockstraw, D.A.; Deng, S.: Silver nanoparticles from ultrasonic spray pyrolysis of aqueous silver nitrate. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 39, 1010–1014 (2005)
Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C.: Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 31, 346–356 (2013)
Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y.: Silver nanoparticles: green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Coll. Interface. Sci. 145, 83–96 (2009)
Jha, A.K.; Prasad, K.; Prasad, K.; Kulkarni, A.: Plant system: nature’s nanofactory. Colloids Surf., B 73, 219–223 (2009)
Mahmood, A.; Sharif, M.; Ahmad, Q.; Mahmood, R.; Riaz, S.; Zafar, M.: Phytochemical analysis and comprehensive evaluation of antimicrobial activity of Nannorhops ritchiana leaves (Mazari palm). World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 6, 173–189 (2017)
Ding, Y.: Organic molecule based chemosensors for biomedical application. Curr. Med. Chem. 26, 3921–3922 (2019)
Koshki, M.; Baghayeri, M.; Fayazi, M.: Application of sepiolite/FeS2 nanocomposite for highly selective detection of mercury(II) based on stripping voltammetric analysis. J. Food Measure. Charact. 15, 5318–5325 (2021)
Baghayeri, M.; Amiri, A.; Karimabadi, F.; Di Masi, S.; Maleki, B.; Adibian, F.; Pourali, A.R.; Malitesta, C.: Magnetic MWCNTs-dendrimer: A potential modifier for electrochemical evaluation of As (III) ions in real water samples. J. Electroanal. Chem. 888, 115059 (2021)
Ichinoki, S.; Kitahata, N.; Fujii, Y.: Selective determination of mercury (II) ion in water by solvent extraction followed by reversed-phase HPLC. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 27, 1785–1798 (2004)
Yang, Q.; Tan, Q.; Zhou, K.; Xu, K.; Hou, X.: Direct detection of mercury in vapor and aerosol from chemical atomization and nebulization at ambient temperature: exploiting the flame atomic absorption spectrometer. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 20, 760–762 (2005)
Kuswandi, B.; Dam, H.H.; Reinhoudt, D.N.; Verboom, W.: Development of a disposable mercury ion-selective optode based on trityl-picolinamide as ionophore. Anal. Chim. Acta 591, 208–213 (2007)
Tao, H.; Lin, Y.; Yan, J.; Di, J.: A plasmonic mercury sensor based on silver–gold alloy nanoparticles electrodeposited on indium tin oxide glass. Electrochem. Commun. 40, 75–79 (2014)
Botasini, S.; Heijo, G.; Méndez, E.: Toward decentralized analysis of mercury (II) in real samples. A critical review on nanotechnology-based methodologies. Anal. Chim. Acta 800, 1–11 (2013)
Rosi, N.L.; Mirkin, C.A.: Nanostructures in biodiagnostics. Chem. Rev. 105, 1547–1562 (2005)
Karimi-Maleh, H.; BeitollahiP, H.; Kumar, S.; Tajik, S.; Jahani, P.M.; Karimi, F.; Karaman, C.; Vasseghian, Y.; Baghayeri, M.; Rouhi, J.; Show, P.L.; Rajendran, S.; Fu, L.; Zare, N.: Recent advances in carbon nanomaterials-based electrochemical sensors for food azo dyes detection. Food Chem. Toxicol. 164, 112961 (2022)
Elahi, N.; Kamali, M.; Baghersad, M.H.: Recent biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles: a review. Talanta 184, 537–556 (2018)
Du, J.; Jiang, L.; Shao, Q.; Liu, X.; Marks, R.S.; Ma, J., et al.: Colorimetric detection of mercury ions based on plasmonic nanoparticles. Small 9, 1467–1481 (2013)
Qin, L.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Huang, D.; Zhang, C.; Xu, P., et al.: A visual application of gold nanoparticles: simple, reliable and sensitive detection of kanamycin based on hydrogen-bonding recognition. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 243, 946–954 (2017)
Raj, D.R.; Prasanth, S.; Vineeshkumar, T.; Sudarsanakumar, C.: Surface plasmon resonance based fiber optic sensor for mercury detection using gold nanoparticles PVA hybrid. Opt. Commun. 367, 102–107 (2016)
Minhaz, A.; Khan, N.; Jamila, N.; Javed, F.; Imran, M.; Shujah, S., et al.: Schiff base stabilized silver nanoparticles as potential sensor for Hg (II) detection, and anticancer and antibacterial agent. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 8898–8908 (2020)
Palanisamy, S.; Zhang, X.; He, T.: Simple colorimetric detection of dopamine using modified silver nanoparticles. SCIENCE CHINA Chem. 59, 387–393 (2016)
Kumar, D.A.; Palanichamy, V.; Roopan, S.M.: Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Alternanthera dentata leaf extract at room temperature and their antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 127, 168–171 (2014)
Tariq, M.; Muhammad, N.; Sirajuddin, M.; Ali, S.; Shah, N.A.; Khalid, N., et al.: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, X-ray structures, biological screenings, DNA interaction study and catalytic activity of organotin (IV) 3-(4-flourophenyl)-2-methylacrylic acid derivatives. J. Organomet. Chem. 723, 79–89 (2013)
Kasap S. O, Principles of Electronic Materials and Devices vol. 2: McGraw-Hill New York, (2006).
A. K. Mittal, A. Kaler, and U. C. Banerjee, "Free radical scavenging and antioxidant activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized from flower extract of Rhododendron dauricum," Nano Biomed. Eng., 4, (2012).
Ravi, S.S.; Christena, L.R.; SaiSubramanian, N.; Anthony, S.P.: Green synthesized silver nanoparticles for selective colorimetric sensing of Hg2+ in aqueous solution at wide pH range. Analyst 138, 4370–4377 (2013)
Deng, L.; Ouyang, X.; Jin, J.; Ma, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, J., et al.: Exploiting the higher specificity of silver amalgamation: selective detection of mercury (II) by forming Ag/Hg amalgam. Anal. Chem. 85, 8594–8600 (2013)
Sebastian, M.; Aravind, A.; Mathew, B.: Green silver-nanoparticle-based dual sensor for toxic Hg (II) ions. Nanotechnology 29, 355502 (2018)
Rastogi, L.; Sashidhar, R.; Karunasagar, D.; Arunachalam, J.: Gum Kondagogu reduced/stabilized silver nanoparticles as direct colorimetric sensor for the sensitive detection of Hg2+ in aqueous system. Talanta 118, 111–117 (2014)
Abbas, K.; Znad, H.; Awual, M.R.: A ligand anchored conjugate adsorbent for effective mercury (II) detection and removal from aqueous media. Chem. Eng. J. 334, 432–443 (2018)
Awual, M.R.: Novel nanocomposite materials for efficient and selective mercury ions capturing from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 307, 456–465 (2017)
Liau, S.; Read, D.; Pugh, W.; Furr, J.; Russell, A.: Interaction of silver nitrate with readily identifiable groups: relationship to the antibacterial action of silver ions. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 25, 279–283 (1997)
Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.; Kim, T.; Kim, J.: A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 52, 662–668 (2000)
Davis, W.; Stout, T.: Disc plate method of microbiological antibiotic assay: II. novel procedure offering improved accuracy. Appl. Microbiol. 22, 666–670 (1971)
Rajarajeswari, C.; Ganeshpandian, M.; Palaniandavar, M.; Riyasdeen, A.; Akbarsha, M.A.: Mixed ligand copper (II) complexes of 1, 10-phenanthroline with tridentate phenolate/pyridyl/(benz) imidazolyl Schiff base ligands: Covalent vs non-covalent DNA binding, DNA cleavage and cytotoxicity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 140, 255–268 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, S., Shujah, S., Nishan, U. et al. Nannorrhops ritchiana Leaf-Based Biomolecular Extract-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles as a Platform for Mercury(II) Sensing, Antimicrobial Activity, and DNA Interaction. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 7673–7684 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07682-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07682-3