Introduction
Operational risk management (ORM) is a crucial aspect of any business, helping organizations identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with their day-to-day operations. By understanding and effectively managing operational risks, businesses can protect their reputation, minimize financial losses, and ensure their long-term success. But before we examine the different types of organizational risk and how they can be mitigated, we must first come to a basic of understanding of the concept.
What is operational risk?
Operational risk refers to the potential for losses resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, systems, or external events. It encompasses a wide range of risks, including human error, technology failures, fraud, legal and compliance issues.
Operational risk is defined as the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events. This definition includes legal risk, but excludes strategic and reputational risk
– Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS)

Types of operational risk
To understand the concept operational risk more clearly, let’s consider a few examples. A manufacturing company may face the risk of equipment breakdown, leading to production delays and financial losses. A retailer might encounter the risk of data breaches, compromising customer information and damaging their reputation. In the banking industry, operational risk could manifest as fraudulent activities, resulting in financial loss.
>> Learn more about types of risk defined in the financial services sector

Understanding the importance of ORM
Operational risk management is vital for organizations across all industries. By implementing an effective ORM framework, businesses can proactively identify potential risks, assess their potential impact, and take appropriate measures to mitigate or even eliminate them altogether. This process enables organizations to enhance their decision-making, improve operational efficiency, and protect their stakeholders’ interests.
Operational risk management is also essential for regulatory compliance. Financial institutions in particular are subject to stringent regulatory requirements; they must demonstrate effective risk management practices to ensure the stability of the financial system and safeguard customer interests. By adhering to regulatory guidelines, organizations can avoid penalties, fines, and reputational damage.
>> Read our article – Understanding Banking Regulatory Requirements for Operational Risk Management

Steps of the ORM Process
The ORM process typically follows a series of steps to ensure comprehensive risk identification, assessment, and mitigation. These steps include:
1. Risk identification
The first step in ORM is identifying potential risks within an organization’s operations. This involves evaluating internal processes, systems, and external factors that could lead to operational failures. Risks can be identified through risk assessments, incident analysis, internal audits, and external benchmarking.
2. Risk assessment
Once risks are identified, organizations must assess their potential impact and likelihood. This involves quantifying risks using various measurement tools and techniques. Risk assessment helps prioritize risks based on the severity of the risk in question, allowing organizations allocate appropriate resources for mitigation.
3. Risk mitigation
After assessing risks, organizations must develop appropriate strategies either to mitigate or (preferably) eliminate them. This may involve implementing control measures, improving internal processes, investing in technology, or transferring risks through insurance. Risk mitigation strategies should be tailored to the specific risks identified and aligned with the organization’s risk appetite.
4. Risk monitoring and reporting
Risk management is an ongoing process. It is essential to monitor and review the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies continually. Regular reporting provides insights into risk trends, emerging risks, and the overall effectiveness of the ORM framework. This information helps organizations make informed decisions and adapt their risk management strategies accordingly.
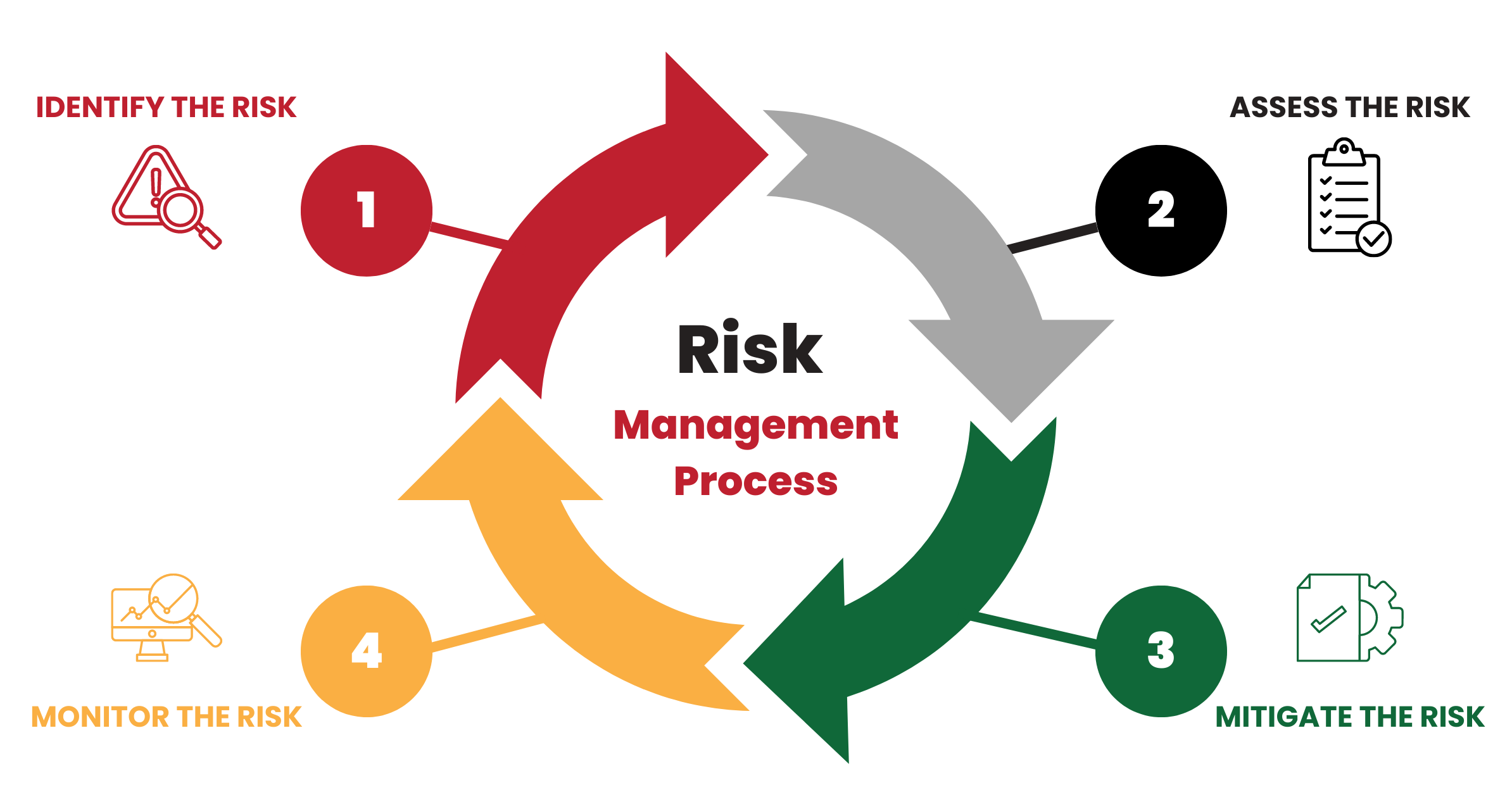
Operational risk management tools and techniques
To enhance the effectiveness of ORM, organizations can leverage various tools and technologies to assess current risks. These include:
- Business process analysis: used to document existing or planned processes to determine ways to improve efficiency and identify risks.
- Risk and control self-assessments: provides subjective assessments of current risk exposures and the state of applicable controls.
- Risk ratings: indicate the severity of the risk, typically on a low-medium-high scale determined by objective thresholds (monetary losses, for example).
- Loss data: provides information on risk events that have already occurred and their financial impact.
- Heat maps: commonly used to present risks in a visual format, plotting risks on a chart with axes of likelihood and impact.
- Key indicators: a monitoring tool used to alert management when a specific risk measurement exceeds a risk tolerance threshold. These include key performance indicators, key risk indicators, and key control indicators.
- Risk register: a tool used to record known risks that shows the likelihood of the risk occurring, any planned action if the risk materializes, the individual or individuals responsible for taking such action, and the timeframe by which the action should be taken.
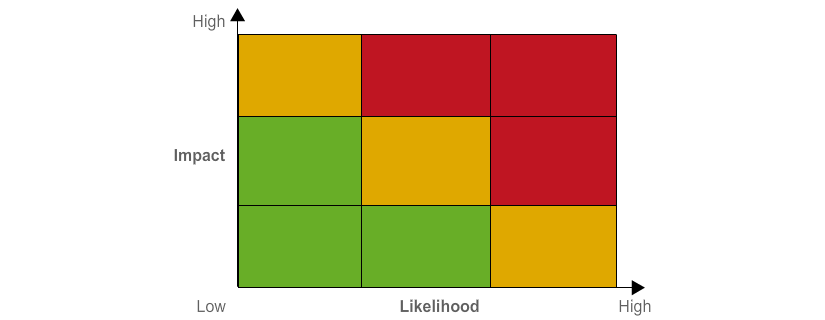
example of a risk heat map
Future operational risk assessment
Operational risks continue to evolve over time, and it is crucial to continue monitoring for changes in operational risk management. Some key techniques to monitor emerging risks include:
- Horizon scanning: This technique, also known as emerging risk analysis, involves identifying and assessing likely developments that could give rise to new operational risks in addition to monitoring new ways of managing these risks.
- Stress testing: The process of stressing values to assess their potential business impact in order to evaluate the strength of current procedures.
- Scenario analysis: Organizations can create hypothetical scenarios to assess the potential impact of specific risks. By simulating various scenarios, organizations can better understand the interdependencies of risks and develop effective effective and timely mitigation strategies.
>> Interested in emerging operational risks in 2023? Read our article

Approaches to managing operational risk
There are a number of broad approaches that a business can adopt when managing operational risk:
- Accept or tolerate the risk as it is within appetite.
- Take one or more actions to reduce the risk.
- Mitigate the risk by taking action to lower the impact of a risk event, or transfer the risk to a third party such as an insurer.
- If the risk is outside appetite and cannot be reduced or mitigated, a business must avoid or exit the risk altogether.
The approach that a business adopts depends on factors such as:
- The size and nature of the risk
- The availability of options to reduce or mitigate the risk and the cost of these options
- The likelihood of a risk event occurring and its potential impact, both of which may change over time

The role of operational risk management in enhancing business resilience
Operational risk management plays a pivotal role in enhancing business resilience. By effectively managing operational risks, organizations can:
- Safeguard their reputation and maintain the trust of stakeholders.
- Minimize financial losses resulting from operational failures.
- Improve decision-making by considering potential risks in strategic planning.
- Enhance operational efficiency by identifying and addressing process inefficiencies.
- Ensure regulatory compliance and avoid penalties and fines.

Conclusion
Operational risk management is a critical element of effective business management. By understanding and navigating the ORM process, organizations can identify, assess, and mitigate operational risks, thereby safeguarding their reputation, protecting stakeholders’ interests, and ensuring long-term success. By incorporating best practices, leveraging appropriate tools and technologies, and staying abreast of emerging trends, organizations can enhance their operational resilience and thrive in an increasingly complex business environment.
Test your knowledge of Operational Risk Management
Navigation menu
IntroductionWhat is operational risk?
Types of operational risk
Understanding the importance of ORM
Steps of the ORM process
Operational risk management tools & techniques
Future operational risk assessment
Approaches to managing operational risk
The role of operational risk management in enhancing business resilience
Test your knowledge of ORM
Learn more about our operational risk management course and resources


