Adopt an Enterprise-wide approach to Model Risk Management
Financial Institutions, even large to mid size in nature, maintain model critical information on a silo’d basis and as a natural extension of the same, the risks arising from these models are also managed on a silo’d basis. For instance, while retail banking division may maintain the model information in a spreadsheet, wholesale banking possibly might have established a more robust solution based approach to capture and maintain model inventory.
Most often, top management of these institutions struggle to get an enterprise-wide view of the risks arising out of models in use across the organization.
More so, it becomes an unmanageable task to gain a holistic view of the model risk arising for themes like CCAR, ICAAP, Loss Forecasting and so on. Regulations such as CCAR, Basel III require financial institutions to adopt an enterprise-wide view of model risk. Hence, there is a need to adopt an enterprise-wide approach when it comes to model risk breaking divisional silos.
There are two core aspects that have to be considered by any institution while striving to adopt an enterprise-wide approach to model risk management namely,
- Model Inventory
- Model Risk Management
Let us look at the model inventory aspects in the following sections:
Centralized Model Repository
In order to adopt an enterprise-wide view of model risk, there arises a need to capture and maintain model information across business groups (such as Wholesale, Retail, Finance, Marketing) and categories (such as Risk, Fraud, Financial Performance, Marketing). With the centralized repository in place, model information can be accessed from a single instance at the click of a button. While doing so, there is a need to identify models using common set of data, assumptions, and limitations.
Establish Model Linkages
Establishing model linkages is the next step. For a model in question, the upstream and downstream linkages have to be clearly identified and established. Upstream models are the ones feeding the model and the downstream models consume the output of the model.
When model linkages are clearly established this can be leveraged extensively while trying to identify set of models affected by flaws in outputs of one or more models.
Model Classification
While establishing a centralized model repository, financial institutions should actively consider creating a unified list of model classification themes across business groups. These classifications should be based on their end use (or) the purpose for which the models were built. All the models captured in the repository have to be classified into one of these themes. Some examples to quote are CCAR, ICAAP, Scoring, Loss Forecasting etc. While models involved in CCAR process may be used across different divisions, when these are grouped on a standard set of themes, a unified model group namely “CCAR models” is established.
Now that a repository with model linkages has been established, it’s time to look at things from a risk perspective.
Model Risk Aggregation
Model risk can’t be limited to risks arising from use of models at a “Model” level. The importance of model risk aggregation can’t be ignored.
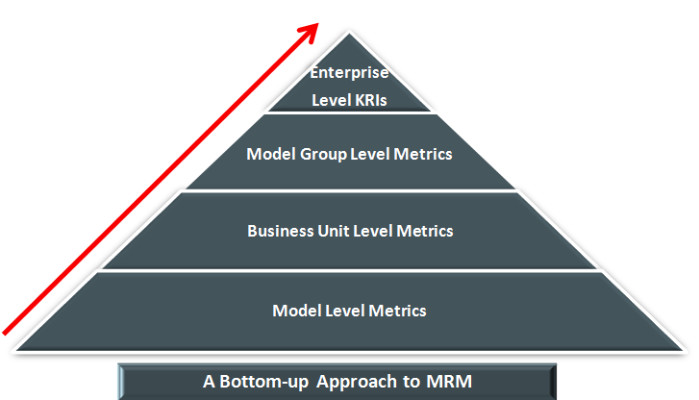
Model risk needs to be aggregated at a model group level across business groups by rolling up validation results across models. While there are no regulatory guidelines available as to how to aggregate model risk, institutions should establish their own set of aggregation methods to gain a holistic view of model risk.
Model Risk Appetite
For any financial institution, the responsibility to prescribe a Risk Appetite statement for model risk lies with the board. As a top down approach, once the risk appetite statement has been established and cascaded down, it is critical to determine risk thresholds and periodic monitoring of the same through KRIs. All metrics need to be rolled up at an enterprise level for comparison with the limits prescribed therein.
Take Action on Group of Models
Finally, with the centralized repository supported by a sound system of model validations and risk aggregation methods in place, here comes the power of analytics. Institutions should be able to analyze and pin point models affected by common set of data, input variables and assumptions. This analysis can translate into taking action on a set of models that are affected such as,
- Looking for opportunities to re-calibrate models,
- Temporary deactivation of models affected from execution or
- Applying an appropriate model overlay on capital charge to account for the risks posed by a group of models
Adopting an Enterprise wide approach to model risk management is expected to provide insights to risks otherwise been overlooked by managing model risk on a silo’d basis at a business unit level. Model risk management is a critical part of enterprise risk management.
Isn’t this the right time your organization adopt an enterprise wide approach to model risk management?
Comments are welcome!!
